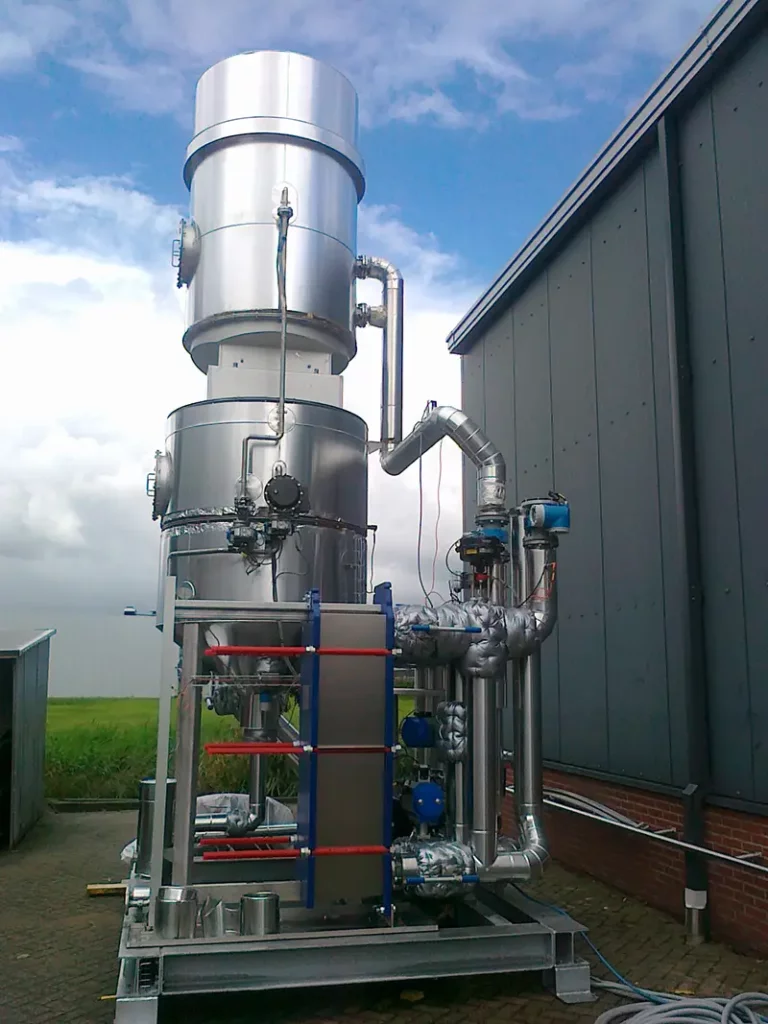
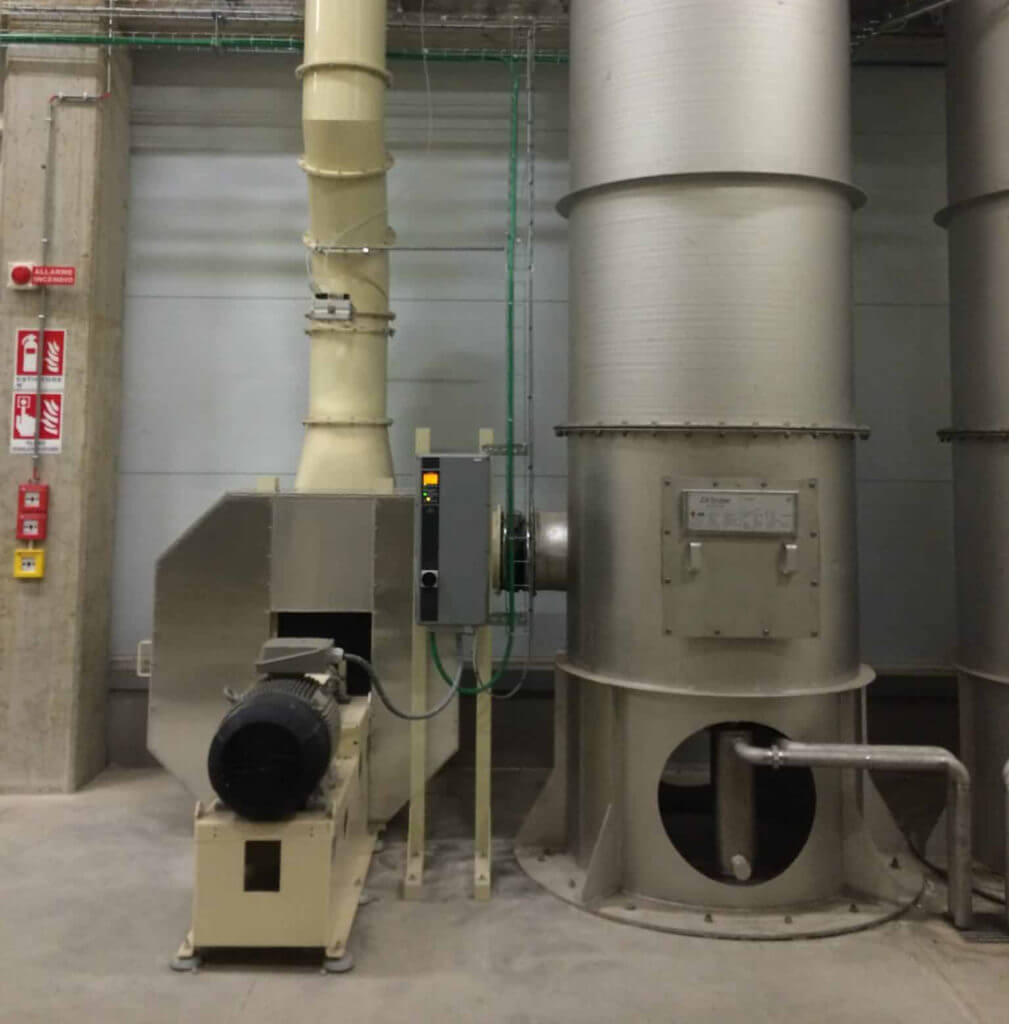
Gas scrubbers are essential for ensuring clean and safe air quality in various industries. Whether you’re considering a wet scrubber, dry scrubber or semi-dry scrubber, this guide will help you make an informed decision.
1. Pollutant type determines which scrubber

Gas scrubbers are pollution control devices designed to remove harmful and unwanted pollutants from exhaust gaseous streams. They come in various types: wet scrubbers, dry scrubbers and semi-dry scrubber. Each type has its strengths and applications.
Contaminant type
The first step in choosing the right industrial scrubber to identify the type of pollutants your process equipment leaves behind in the exhaust stream(s). Certain types of scrubbers can be highly effective for capturing specific contaminants, such as particulate matter, fine droplets (liquid carryover), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and many others. Identifying the pollutant content and makeup of the exhaust gas is crucial for the selecting the right gas-scrubbing approach.
Scrubber type
Once you’ve identified the pollutant type, it is possible to select the appropriate scrubber. There are three main categories where gas scrubbers can be divided into:
- Wet Scrubber
- Dry Scrubbers
- Semi-dry Scrubbers
Wet scrubbers are used to clean gas streams by removing particulate and gaseous pollutants using liquid, usually water or a caustic solution. Various scrubber designs aim for high pollutant removal efficiencies, often exceeding 95%.
Dry and semi-dry scrubbing systems rely on absorption or adsorption of pollutant onto specialized sorbents. Some dry scrubbers also introduce the sorbent as powder to improve the absorption efficiency. In the case of semi-dry scrubbers, a certain amount of moisture is introduced into the exhaust stream, together with the sorbent material, without reaching the dew point.
Each type of industrial scrubbers has its strengths and is tailored to particular applications.
2. Size and Capacity
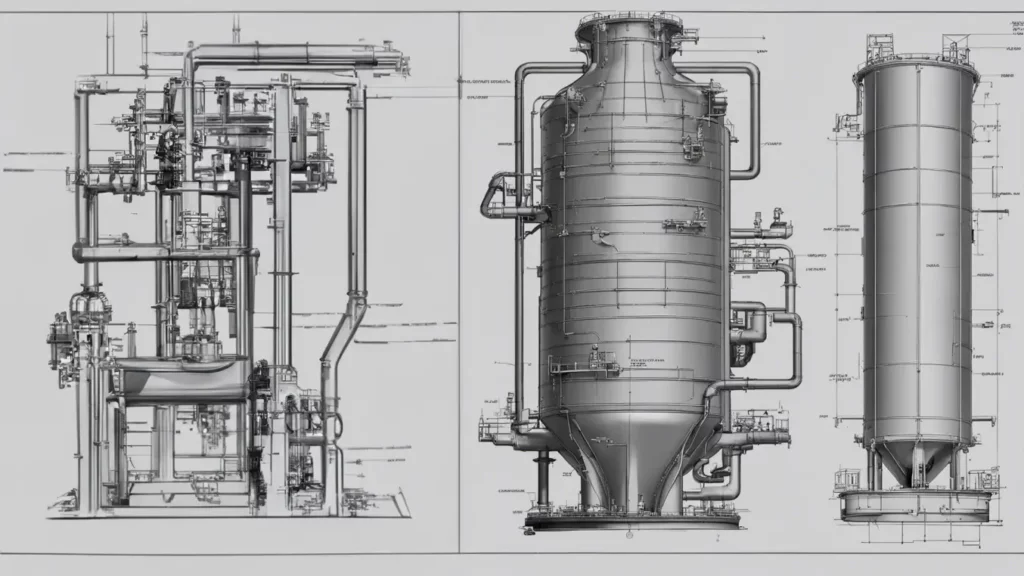
After identifying the suitable gas scrubber type, there are two factors to carefully assess into the design: the scrubber’s flow capacity and footprint.
Flow capacity
One of the design parameters that dictates the design for a gas scrubber is the amount of flow capacity to be treated. Based on a given flow capacity and gas composition, it will also be possible to determine the necessary amount of scrubbing liquid or adsorbent needed for the scrubber to operate effectively. A gas scrubber should be tailored in alignment with your unique requirements.
Footprint of scrubber
The design flow capacity of a given scrubber is in general proportional to the amount of footprint to be provided. Hence, the placement of a scrubber needs to be well considered, accounting for distance between the scrubber and the source of the waste stream, space availability surrounding the process equipment, provision of utilities (e.g., scrubbing liquid connections), and many more.
3. Compliance
Compliance with regulatory pollution control is a must. Your selected industrial air scrubber should align with both local and international emissions standards. It is a legal obligation as regulations and emissions standards are in place to safeguard the environment and public health. Failing to comply can result in legal consequences and financial penalties. Beyond the legal aspect, compliance reflects a commitment to environmental responsibility, showcasing a company’s dedication to reducing the environmental impact of its industrial processes.
4. Environmental impact
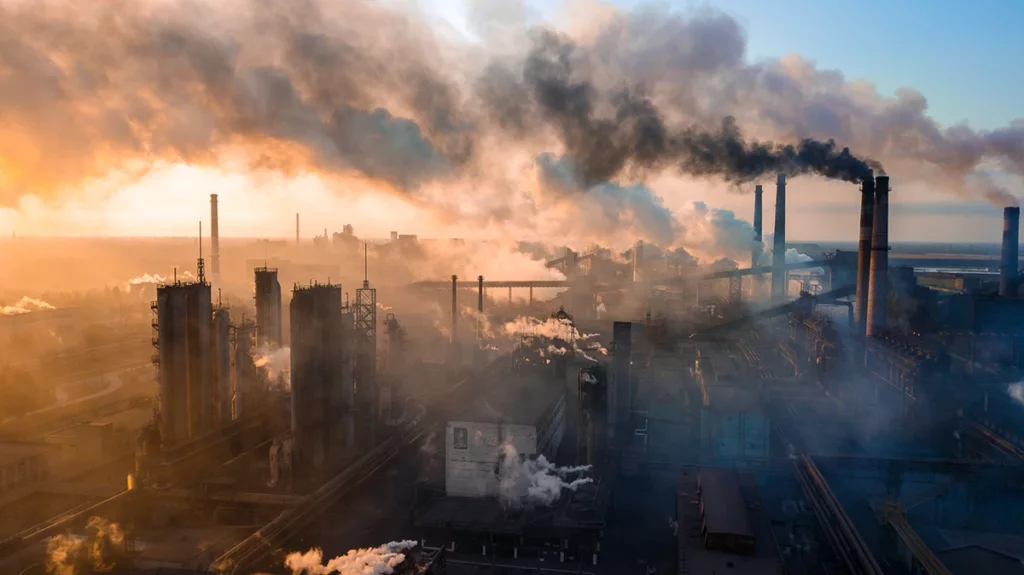

Scrubbers play a crucial role in reducing pollution but also come with environmental impacts with waste treatment. Responsible management is vital for sustainable operations.
Wet scrubber – water treatment
If you opt for a wet scrubber, be prepared to address water treatment. Wet scrubbers generate wastewater that needs proper management. Effective water treatment solutions are essential to handle this byproduct responsibly and prevent environmental harm.
Dry-scrubbing – Waste collection
The waste generated in dry scrubber systems primarily consists of the solid byproducts created during the gas-neutralization process. These byproducts are typically collected in hoppers or chambers within the scrubber system and then removed for disposal. It’s crucial to manage and dispose of these waste materials properly to ensure environmental compliance and safety.
5. Buying and operating cost
Consider not only the initial purchase cost but also the long-term operating expenses associated with your industrial air scrubber. Efficient scrubbers can lead to significant cost savings in the long run. Be sure to assess the total cost of ownership and factor it into your decision-making process.
Service – Global Support
Post-purchase support is critical for the efficient and reliable operation of your scrubber system. Look for a supplier that offers global support and maintenance services. Reliable service ensures that your scrubber continues to meet your emission control needs over time.
Adapting to Unique Emission Challenges
Every industrial situation is unique, with varying gas emissions and environmental requirements. JOA understands the importance of careful consideration and precise calculations in addressing these differences. With over 25 years of experience, JOA has built a strong reputation for providing tailored solutions based on data-driven assessments and air technical modeling. Please contact us if you need an expert on scrubbing technology for your emission challenge.


