Industrial facilities are the backbone of the manufacturing sector but they also pose significant challenges in terms of air pollution control. Among the most effective solutions to mitigate these emissions are industrial wet scrubbers. These systems play a crucial role in ensuring clean and safe air quality by removing harmful pollutants from exhaust gases before they are released into the atmosphere. But how exactly does an industrial wet scrubber work? Let’s dive into the mechanics and functions of these indispensable air pollution control devices.
Table of Contents
What is a wet scrubber used for?
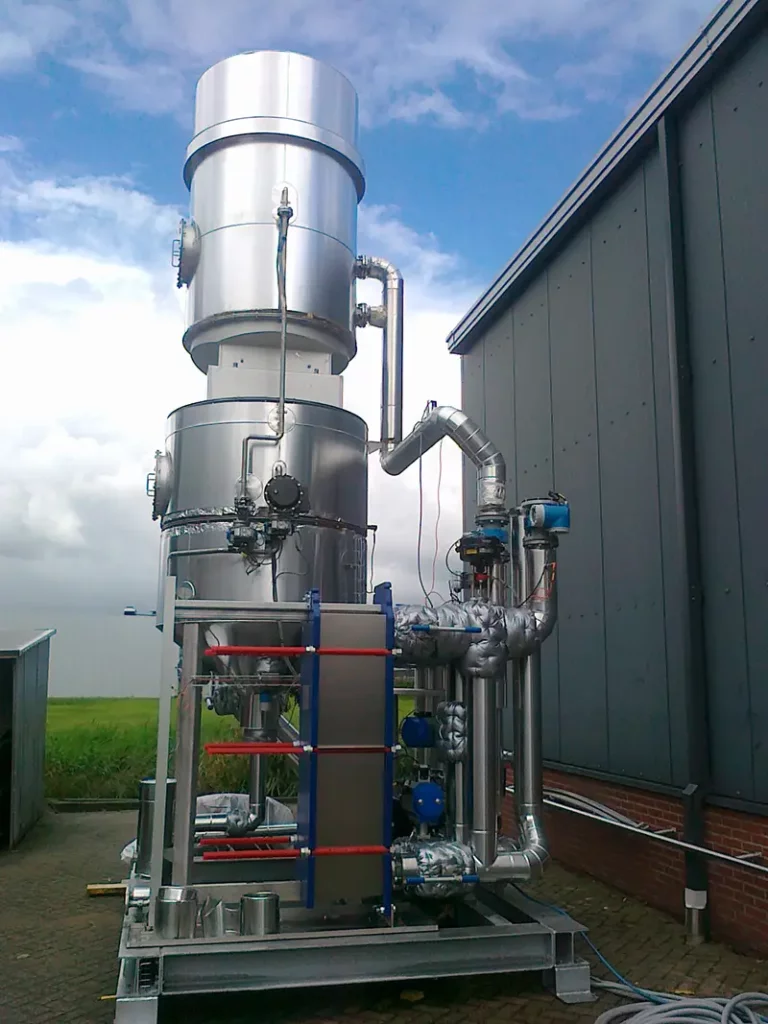
At its core, an industrial wet scrubber is a system designed to remove particulate matter and gas pollutants from industrial exhaust streams, like SO₂. It uses a liquid (most commonly water) to capture and remove contaminants, ensuring that only clean air is released into the environment.
The versatility and efficiency of wet scrubbers have made them essential equipment in various industries, such as chemical, pharmaceutical, and food production, to name just a few.
The basic operation of a wet scrubber
The operation of an industrial wet scrubber can be divided into several key stages:
- Exhaust Gas Introduction: The contaminated exhaust gas is funneled into the scrubber system, where it is met with a scrubbing liquid. This is often achieved using a fan or blower system to ensure that the gas flows through the scrubber at an optimal rate.
- Contact With Scrubbing Liquid: The core of the wet scrubbing process is the intimate contact between the polluted gas stream and the scrubbing liquid. This interaction can take place in various ways, depending on the scrubber design. Common methods include spray towers, where the liquid is sprayed into the gas, and packed towers, where the gas passes through a wet packed bed.
- Pollutant Capture: As the gas interacts with the scrubbing liquid, pollutants are transferred from the gas phase to the liquid phase. This transfer can occur through physical processes such as impaction and absorption, or chemical reactions, particularly if the scrubbing liquid contains reactive agents tailored to neutralize specific pollutants.
- Separation and Discharge: After the gas has been cleaned, it is separated from the now-contaminated scrubbing liquid. The cleaned gas exits the system and is released into the atmosphere, while the dirty liquid is collected for recirculation, treatment or disposal. Efficient separation is crucial to prevent liquid droplets from escaping with the gas.
- Liquid Treatment and Recirculation: The contaminated scrubbing liquid is treated to remove the captured pollutants. In many cases, the liquid can be recycled and reused within the scrubber, reducing waste and operational costs. It is also possible to reuse the heat that has been absorbed by the scrubbing liquid for other purposes.

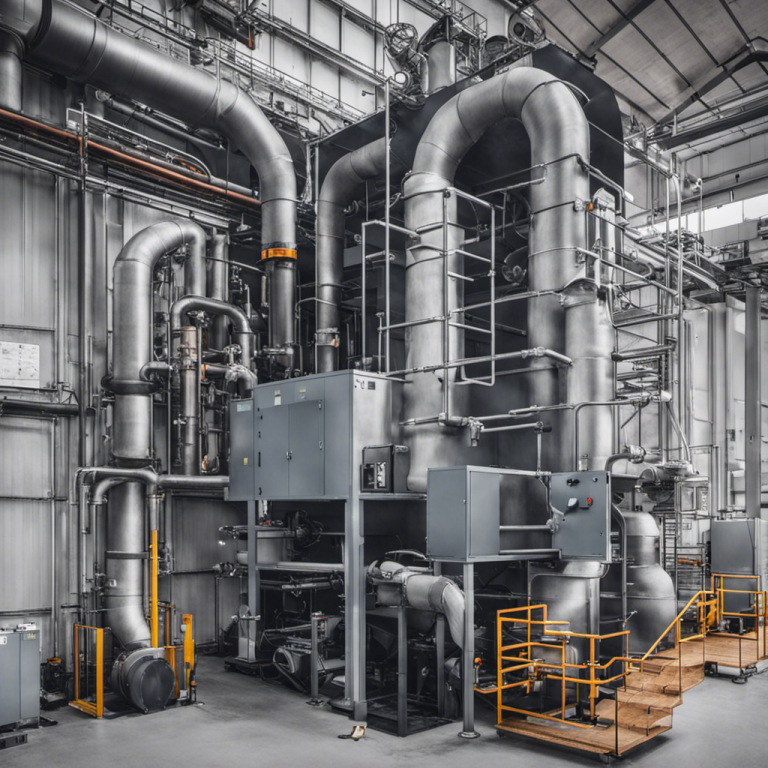
A few examples of industrial wet scrubbers
Industrial wet scrubbers come in various designs, each tailored to specific types of pollutants and industrial applications:
- Venturi Scrubbers: Ideal for particulate-heavy exhaust streams, venturi scrubbers use a narrow throat to accelerate the gas-liquid interaction, enhancing pollutant capture efficiency.
- Inline Venturi Scrubber: A specialised venturi scrubber where the throat is incoporated inside the scrubbing tower. Read more about this specific scrubber here.
- Packed Tower Scrubbers: Suited for gaseous pollutants, these scrubbers force the exhaust through a tower filled with packing material, maximizing gas-liquid contact.
- Spray Tower Scrubbers: These systems use nozzles to spray scrubbing liquid directly into the gas stream, a straightforward and effective method for a wide range of applications.
WEBINAR HEAT RECOVERY
Learn how to capture energy from exhaust gas to meet EU green goals and cut costs. Covers techniques for low/medium temp waste heat and how to handle challenges like variable loads and corrosion.
The Importance of Wet Scrubbers in Industrial Pollution Control
Industrial wet scrubbers are more than just air pollution control devices; they are a testament to the commitment of industries to environmental stewardship and public health. By efficiently removing harmful pollutants from exhaust gases, wet scrubbers play a critical role in reducing the environmental impact of industrial operations and ensuring compliance with air quality regulations.
In conclusion, the function of industrial wet scrubbers is a fascinating interplay of chemistry and engineering, offering a robust solution for air pollution control. As industries continue to evolve and environmental regulations become more stringent, the role of wet scrubbers in maintaining clean air and protecting the environment will only grow in importance.
Which industrial scrubber do I need?
You might be asking yourself, “Which type of scrubber is right for me?” Because It’s essential to match the correct scrubber to your unique production process. At JOA, our approach is rooted in data, guiding us to pinpoint the exact scrubber type that aligns with your needs. Through pre-engineering studies, we identify the solution that seamlessly integrates into your operation, ensuring optimal performance and sustainability.
Partnering with JOA Air Solutions means that your air pollution challenge is precisely tailored to your needs, resulting in a durable solution. So please share you challenge with us and see how we can help you improve your site.